Update files
parent
8986dfce3c
commit
923cfcb835
98
README.md
98
README.md
|
|
@ -1,19 +1,95 @@
|
|||
# USB Power Tester based on ATtiny45/85
|
||||
Simple USB Power Tester based on ATtiny45/85 andINA219. You can switch between different screens by pressing the SET button.
|
||||
# USB Power Tester based on ATtiny25/45/85
|
||||
Simple USB Power Tester based on ATtiny25/45/85 and INA219. The device measures voltage, current, power, energy, capacity and displays the values on an OLED screen. You can switch between different screens by pressing the SET button.
|
||||
|
||||
Project Video: https://youtu.be/QKx8Vn_IfjU
|
||||
- Project Video (YouTube): https://youtu.be/QKx8Vn_IfjU
|
||||
- Project Files (EasyEDA): https://easyeda.com/wagiminator/attiny85-usb-tester
|
||||
|
||||
Project at EasyEDA: https://easyeda.com/wagiminator/attiny85-usb-tester
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# Hardware
|
||||
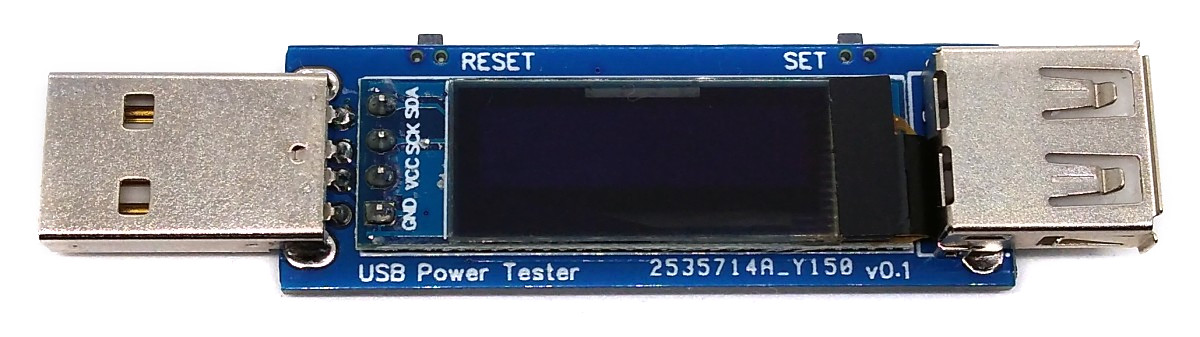
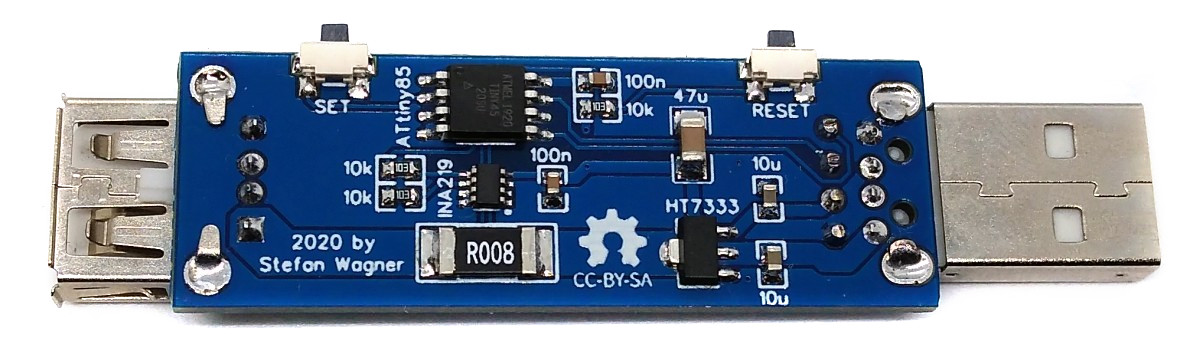
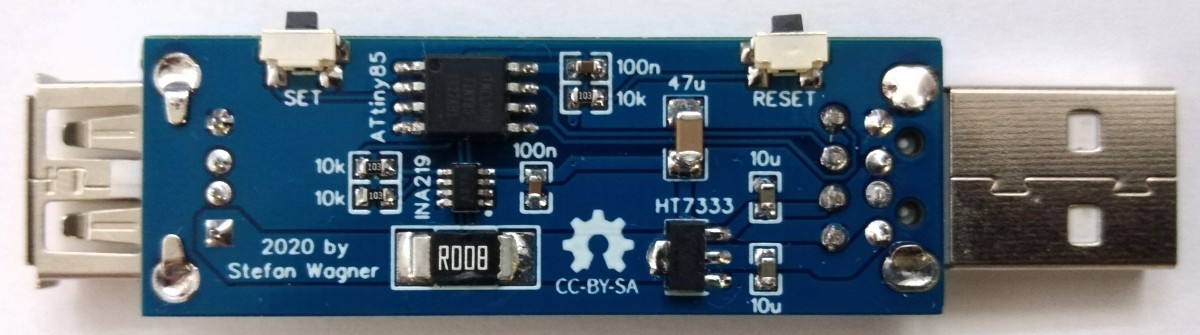
## USB Connectors
|
||||
The device is equipped with a USB-A plug for the input and a USB-A socket for the output, so that it can be plugged between the power supply and the consumer. D+ and D- are passed through so that the consumer can negotiate the charging protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
## Voltage and Current Measurement
|
||||
An [INA219](https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/ina219.pdf) is used to measure voltage and current. The INA219 is a current shunt and power monitor with an I²C-compatible interface. The device monitors both shunt voltage drop and bus supply voltage, with programmable conversion times and filtering. A programmable calibration value, combined with an internal multiplier, enables direct readouts of current in amperes. The selected shunt resistance of 8 milliohms enables both a very small influence on the circuit and a measurement with a resolution of 1 milliampere. For an accurate measurement, a shunt resistor with a low tolerance (1% or better) should be selected.
|
||||
|
||||
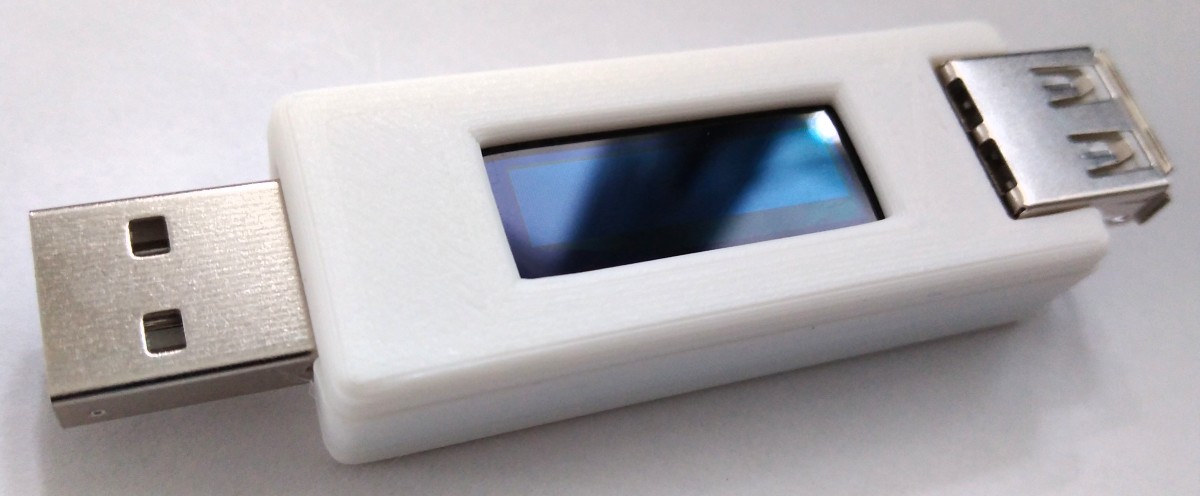
## User Interface
|
||||
The user interface utilizes two buttons and a [128x64 pixels OLED display](http://aliexpress.com/wholesale?SearchText=128+64+0.96+oled+new+4pin). An [ATtiny24/45/85](https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/Atmel-2586-AVR-8-bit-Microcontroller-ATtiny25-ATtiny45-ATtiny85_Datasheet.pdf) microcontroller handles the user interface as well as the calculation and display of the values.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Software
|
||||
## Basic Principle
|
||||
The INA219 continuously measures current and voltage and transmits the values to the ATtiny via I²C. From this, the ATtiny calculates the other values and displays them on the OLED screen.
|
||||
|
||||
## I²C OLED Implementation
|
||||
The I²C protocol implementation is based on a crude bitbanging method. It was specifically designed for the limited resources of ATtiny10 and ATtiny13, but it works with some other AVRs (including the ATtiny25/45/85) as well. The functions for the OLED are adapted to the SSD1306 OLED module, but they can easily be modified to be used for other modules. In order to save resources, only the basic functionalities which are needed for this application are implemented. For a detailed information on the working principle of the I²C OLED implementation visit [TinyOLEDdemo](https://github.com/wagiminator/attiny13-tinyoleddemo).
|
||||
|
||||
## Accuracy of Time and Capacity Determination
|
||||
The internal oscillator of the ATtiny is used to determine energy and capacity. The accuracy of the internal oscillator is +/-10% with the factory calibration. This can be improved to +/-2% or better by [manual calibration](https://github.com/wagiminator/ATtiny84-TinyCalibrator). The calibration value determined in this way can be set in the source code.
|
||||
|
||||
## Compiling and Uploading
|
||||
Since there is no ICSP header on the board, you have to program the ATtiny either before soldering using an [SOP adapter](https://aliexpress.com/wholesale?SearchText=sop-8+150mil+adapter), or after soldering using an [EEPROM clip](https://aliexpress.com/wholesale?SearchText=sop8+eeprom+programming+clip). The [AVR Programmer Adapter](https://github.com/wagiminator/AVR-Programmer/tree/master/AVR_Programmer_Adapter) can help with this.
|
||||
|
||||
### If using the Arduino IDE
|
||||
- Make sure you have installed [ATtinyCore](https://github.com/SpenceKonde/ATTinyCore).
|
||||
- Go to **Tools -> Board -> ATtinyCore** and select **ATtiny25/45/85 (No bootloader)**.
|
||||
- Go to **Tools** and choose the following board options:
|
||||
- **Chip:** ATtiny25 or 45 or 85 (depending on your chip)
|
||||
- **Clock:** 8 MHz (internal)
|
||||
- **Millis/Micros:** disabled
|
||||
- **B.O.D.Level:** B.O.D. enabled (2.7V)
|
||||
- Leave the rest at the default settings
|
||||
- Connect your programmer to your PC and to the ATtiny.
|
||||
- Go to **Tools -> Programmer** and select your ISP programmer (e.g. [USBasp](https://aliexpress.com/wholesale?SearchText=usbasp)).
|
||||
- Go to **Tools -> Burn Bootloader** to burn the fuses.
|
||||
- Open USB_Tester sketch and click **Upload**.
|
||||
|
||||
### If using the precompiled hex-file
|
||||
- Make sure you have installed [avrdude](https://learn.adafruit.com/usbtinyisp/avrdude).
|
||||
- Connect your programmer to your PC and to the ATtiny.
|
||||
- Open a terminal.
|
||||
- Navigate to the folder with the hex-file.
|
||||
- Execute the following command (if necessary replace "usbasp" with the programmer you use):
|
||||
```
|
||||
avrdude -c usbasp -p t85 -U lfuse:w:0xe2:m -U hfuse:w:0xd5:m -U efuse:w:0xff:m -U flash:w:usb_tester.hex
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### If using the makefile (Linux/Mac)
|
||||
- Make sure you have installed [avr-gcc toolchain and avrdude](http://maxembedded.com/2015/06/setting-up-avr-gcc-toolchain-on-linux-and-mac-os-x/).
|
||||
- Connect your programmer to your PC and to the ATtiny.
|
||||
- Open the makefile and change the chip if you are not using ATtiny85 and the programmer if you are not using usbasp.
|
||||
- Open a terminal.
|
||||
- Navigate to the folder with the makefile and the Arduino sketch.
|
||||
- Run "make install" to compile, burn the fuses and upload the firmware.
|
||||
|
||||
# Operating Instructions
|
||||
1. Connect the device between a power supply and a consumer.
|
||||
2. Use the SET button to switch between the different screens.
|
||||
3. Use the RESET button to reset all values.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# Characteristics
|
||||
|Parameter|Value|
|
||||
|-|-|
|
||||
|Voltage|3V - 12V|
|
||||
|Current|max 5A|
|
||||
|Resolution|4mV / 1mA|
|
||||
|Voltage Measurement Resolution|4mV|
|
||||
|Current Measurement Resolution|1mA|
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
# References, Links and Notes
|
||||
1. [UBS-C Version](https://github.com/wagiminator/ATtiny85-USB-C-Tester)
|
||||
2. [ATtiny25/45/85 Datasheet](https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/Atmel-2586-AVR-8-bit-Microcontroller-ATtiny25-ATtiny45-ATtiny85_Datasheet.pdf)
|
||||
3. [INA219 Datasheet](https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/ina219.pdf)
|
||||
4. [SSD1306 Datasheet](https://cdn-shop.adafruit.com/datasheets/SSD1306.pdf)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# License
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
|
||||
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 90 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 94 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 66 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 98 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 87 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 100 KiB |
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,475 @@
|
|||
// USB Power Tester - Basic
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This code implements the basic functionality for the USB Power Tester.
|
||||
// It reads voltage, current and power from the INA219, calculates
|
||||
// capacity and shows the values on the OLED. The SET button is used to
|
||||
// switch between different screens.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// +-\/-+
|
||||
// RESET --- A0 (D5) PB5 1| |8 Vcc
|
||||
// SET ----- A3 (D3) PB3 2| |7 PB2 (D2) A1 ---- OLED/INA (SCK)
|
||||
// A2 (D4) PB4 3| |6 PB1 (D1)
|
||||
// GND 4| |5 PB0 (D0) ------- OLED/INA (SDA)
|
||||
// +----+
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Core: ATtinyCore (https://github.com/SpenceKonde/ATTinyCore)
|
||||
// Board: ATtiny25/45/85 (No bootloader)
|
||||
// Chip: ATtiny25 or 45 or 85 (depending on your chip)
|
||||
// Clock: 8 MHz (internal)
|
||||
// Millis: disabled
|
||||
// B.O.D.: 2.7V
|
||||
// Leave the rest on default settings. Don't forget to "Burn bootloader" !
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The I²C OLED implementation is based on TinyOLEDdemo
|
||||
// https://github.com/wagiminator/ATtiny13-TinyOLEDdemo
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 2020 by Stefan Wagner
|
||||
// Project Files (EasyEDA): https://easyeda.com/wagiminator
|
||||
// Project Files (Github): https://github.com/wagiminator
|
||||
// License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// oscillator calibration value (uncomment and set if necessary)
|
||||
//#define OSCCAL_VAL 0x48
|
||||
|
||||
// Libraries
|
||||
#include <avr/io.h>
|
||||
#include <avr/pgmspace.h>
|
||||
#include <avr/interrupt.h>
|
||||
#include <util/delay.h>
|
||||
|
||||
// Pin definitions
|
||||
#define I2C_SDA PB0 // I2C serial data pin
|
||||
#define I2C_SCL PB2 // I2C serial clock pin
|
||||
#define SETBUTTON PB3 // SET button
|
||||
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
// I2C Implementation
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C macros
|
||||
#define I2C_SDA_HIGH() DDRB &= ~(1<<I2C_SDA) // release SDA -> pulled HIGH by resistor
|
||||
#define I2C_SDA_LOW() DDRB |= (1<<I2C_SDA) // SDA as output -> pulled LOW by MCU
|
||||
#define I2C_SCL_HIGH() DDRB &= ~(1<<I2C_SCL) // release SCL -> pulled HIGH by resistor
|
||||
#define I2C_SCL_LOW() DDRB |= (1<<I2C_SCL) // SCL as output -> pulled LOW by MCU
|
||||
#define I2C_SDA_READ() (PINB & (1<<I2C_SDA)) // read SDA line
|
||||
#define I2C_DELAY() asm("lpm") // delay 3 clock cycles
|
||||
#define I2C_CLOCKOUT() I2C_SCL_HIGH();I2C_DELAY();I2C_SCL_LOW() // clock out
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C init function
|
||||
void I2C_init(void) {
|
||||
DDRB &= ~((1<<I2C_SDA)|(1<<I2C_SCL)); // pins as input (HIGH-Z) -> lines released
|
||||
PORTB &= ~((1<<I2C_SDA)|(1<<I2C_SCL)); // should be LOW when as ouput
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C transmit one data byte to the slave, ignore ACK bit, no clock stretching allowed
|
||||
void I2C_write(uint8_t data) {
|
||||
for(uint8_t i=8; i; i--, data<<=1) { // transmit 8 bits, MSB first
|
||||
(data & 0x80) ? (I2C_SDA_HIGH()) : (I2C_SDA_LOW()); // SDA HIGH if bit is 1
|
||||
I2C_CLOCKOUT(); // clock out -> slave reads the bit
|
||||
}
|
||||
I2C_DELAY(); // delay 3 clock cycles
|
||||
I2C_SDA_HIGH(); // release SDA for ACK bit of slave
|
||||
I2C_CLOCKOUT(); // 9th clock pulse is for the ignored ACK bit
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C start transmission
|
||||
void I2C_start(uint8_t addr) {
|
||||
I2C_SDA_LOW(); // start condition: SDA goes LOW first
|
||||
I2C_SCL_LOW(); // start condition: SCL goes LOW second
|
||||
I2C_write(addr); // send slave address
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C restart transmission
|
||||
void I2C_restart(uint8_t addr) {
|
||||
I2C_SDA_HIGH(); // prepare SDA for HIGH to LOW transition
|
||||
I2C_SCL_HIGH(); // restart condition: clock HIGH
|
||||
I2C_start(addr); // start again
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C stop transmission
|
||||
void I2C_stop(void) {
|
||||
I2C_SDA_LOW(); // prepare SDA for LOW to HIGH transition
|
||||
I2C_SCL_HIGH(); // stop condition: SCL goes HIGH first
|
||||
I2C_SDA_HIGH(); // stop condition: SDA goes HIGH second
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C receive one data byte from the slave (ack=0 for last byte, ack>0 if more bytes to follow)
|
||||
uint8_t I2C_read(uint8_t ack) {
|
||||
uint8_t data = 0; // variable for the received byte
|
||||
I2C_SDA_HIGH(); // release SDA -> will be toggled by slave
|
||||
for(uint8_t i=8; i; i--) { // receive 8 bits
|
||||
data<<=1; // bits shifted in right (MSB first)
|
||||
I2C_DELAY(); // delay 3 clock cycles
|
||||
I2C_SCL_HIGH(); // clock HIGH
|
||||
if(I2C_SDA_READ()) data |=1; // read bit
|
||||
I2C_SCL_LOW(); // clock LOW -> slave prepares next bit
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (ack) I2C_SDA_LOW(); // pull SDA LOW to acknowledge (ACK)
|
||||
I2C_DELAY(); // delay 3 clock cycles
|
||||
I2C_CLOCKOUT(); // clock out -> slave reads ACK bit
|
||||
return(data); // return the received byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
// OLED Implementation
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED definitions
|
||||
#define OLED_ADDR 0x78 // OLED write address
|
||||
#define OLED_CMD_MODE 0x00 // set command mode
|
||||
#define OLED_DAT_MODE 0x40 // set data mode
|
||||
#define OLED_INIT_LEN 11 // 9: no screen flip, 11: screen flip
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED init settings
|
||||
const uint8_t OLED_INIT_CMD[] PROGMEM = {
|
||||
0xA8, 0x1F, // set multiplex for 128x32
|
||||
0x20, 0x01, // set vertical memory addressing mode
|
||||
0xDA, 0x02, // set COM pins hardware configuration to sequential
|
||||
0x8D, 0x14, // enable charge pump
|
||||
0xAF, // switch on OLED
|
||||
0xA1, 0xC8 // flip the screen
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED 6x16 font
|
||||
const uint8_t OLED_FONT[] PROGMEM = {
|
||||
0x7C, 0x1F, 0x02, 0x20, 0x02, 0x20, 0x02, 0x20, 0x02, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 0 0
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 1 1
|
||||
0x00, 0x1F, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x00, // 2 2
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 3 3
|
||||
0x7C, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 4 4
|
||||
0x7C, 0x00, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x00, 0x1F, // 5 5
|
||||
0x7C, 0x1F, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x00, 0x1F, // 6 6
|
||||
0x7C, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 7 7
|
||||
0x7C, 0x1F, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 8 8
|
||||
0x7C, 0x00, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 9 9
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0xF0, 0x3F, 0x8C, 0x00, 0x82, 0x00, 0x8C, 0x00, 0xF0, 0x3F, // 10 A
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0xFE, 0x07, 0x00, 0x18, 0x00, 0x20, 0x00, 0x18, 0xFE, 0x07, // 11 V
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0xFE, 0x1F, 0x00, 0x20, 0x00, 0x1F, 0x00, 0x20, 0xFE, 0x1F, // 12 W
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0xFE, 0x3F, 0x00, 0x01, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x00, 0x3F, // 13 h
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x80, 0x3F, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x3F, 0x80, 0x00, 0x00, 0x3F, // 14 m
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x30, 0x00, 0x30, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, // 15 .
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x30, 0x06, 0x30, 0x06, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, // 16 :
|
||||
0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, // 17 -
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 // 18 SPACE
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Character definitions
|
||||
#define DECIMAL 15
|
||||
#define COLON 16
|
||||
#define SPACE 18
|
||||
|
||||
// For BCD conversion
|
||||
const uint16_t divider[5] = {10000, 1000, 100, 10, 1};
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED init function
|
||||
void OLED_init(void) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_CMD_MODE); // set command mode
|
||||
for (uint8_t i=0; i<OLED_INIT_LEN; i++)
|
||||
I2C_write(pgm_read_byte(&OLED_INIT_CMD[i])); // send the command bytes
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED set the cursor
|
||||
void OLED_setCursor(uint8_t xpos, uint8_t ypos) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_CMD_MODE); // set command mode
|
||||
I2C_write(0x22); // command for min/max page
|
||||
I2C_write(ypos); I2C_write(ypos+1); // min: ypos; max: ypos+1
|
||||
I2C_write(xpos & 0x0F); // set low nibble of start column
|
||||
I2C_write(0x10 | (xpos >> 4)); // set high nibble of start column
|
||||
I2C_write(0xB0 | (ypos)); // set start page
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED clear screen
|
||||
void OLED_clearScreen(void) {
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(0, 0); // set cursor at upper half
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
uint8_t i = 0; // count variable
|
||||
do {I2C_write(0x00);} while (--i); // clear upper half
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(0, 2); // set cursor at lower half
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
do {I2C_write(0x00);} while (--i); // clear upper half
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED plot a character
|
||||
void OLED_plotChar(uint8_t ch) {
|
||||
ch = (ch << 3) + (ch << 2); // calculate position of character in font array
|
||||
I2C_write(0x00); I2C_write(0x00); // print spacing between characters
|
||||
for(uint8_t i=12; i; i--) I2C_write(pgm_read_byte(&OLED_FONT[ch++])); // print character
|
||||
I2C_write(0x00); I2C_write(0x00); // print spacing between characters
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED print a character
|
||||
void OLED_printChar(uint8_t ch) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
OLED_plotChar(ch); // plot the character
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED print a string from program memory; terminator: 255
|
||||
void OLED_printPrg(const uint8_t* p) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
uint8_t ch = pgm_read_byte(p); // read first character from program memory
|
||||
while (ch < 255) { // repeat until string terminator
|
||||
OLED_plotChar(ch); // plot character on OLED
|
||||
ch = pgm_read_byte(++p); // read next character
|
||||
}
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED print 16-bit value as 5-digit decimal (BCD conversion by substraction method)
|
||||
void OLED_printDec16(uint16_t value) {
|
||||
uint8_t leadflag = 0; // flag for leading spaces
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
for(uint8_t digit = 0; digit < 5; digit++) { // 5 digits
|
||||
uint8_t digitval = 0; // start with digit value 0
|
||||
while (value >= divider[digit]) { // if current divider fits into the value
|
||||
leadflag = 1; // end of leading spaces
|
||||
digitval++; // increase digit value
|
||||
value -= divider[digit]; // decrease value by divider
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (leadflag || (digit == 4)) OLED_plotChar(digitval); // print the digit
|
||||
else OLED_plotChar(SPACE); // or print leading space
|
||||
}
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED print 16-bit value as 3-digit decimal (BCD conversion by substraction method)
|
||||
void OLED_printDec12(uint16_t value) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
for(uint8_t digit = 2; digit < 5; digit++) { // 3 digits
|
||||
uint8_t digitval = 0; // start with digit value 0
|
||||
while (value >= divider[digit]) { // if current divider fits into the value
|
||||
digitval++; // increase digit value
|
||||
value -= divider[digit]; // decrease value by divider
|
||||
}
|
||||
OLED_plotChar(digitval); // print the digit
|
||||
}
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED print 8-bit value as 2-digit decimal (BCD conversion by substraction method)
|
||||
void OLED_printDec8(uint8_t value) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
uint8_t digitval = 0; // start with digit value 0
|
||||
while (value >= 10) { // if current divider fits into the value
|
||||
digitval++; // increase digit value
|
||||
value -= 10; // decrease value by divider
|
||||
}
|
||||
OLED_plotChar(digitval); // print first digit
|
||||
OLED_plotChar(value); // print second digit
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
// INA219 Implementation
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 register values
|
||||
#define INA_ADDR 0x80 // I2C write address of INA219
|
||||
#define INA_CONFIG 0b0000011001100111 // INA config register according to datasheet
|
||||
#define INA_CALIB 5120 // INA calibration register according to R_SHUNT
|
||||
#define INA_REG_CONFIG 0x00 // INA configuration register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_CALIB 0x05 // INA calibration register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_SHUNT 0x01 // INA shunt voltage register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_VOLTAGE 0x02 // INA bus voltage register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_POWER 0x03 // INA power register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_CURRENT 0x04 // INA current register address
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 write a register value
|
||||
void INA_write(uint8_t reg, uint16_t value) {
|
||||
I2C_start(INA_ADDR); // start transmission to INA219
|
||||
I2C_write(reg); // write register address
|
||||
I2C_write(value >> 8); // write register content high byte
|
||||
I2C_write(value); // write register content low byte
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 read a register
|
||||
uint16_t INA_read(uint8_t reg) {
|
||||
uint16_t result; // result variable
|
||||
I2C_start(INA_ADDR); // start transmission to INA219
|
||||
I2C_write(reg); // write register address
|
||||
I2C_restart(INA_ADDR | 0x01); // restart for reading
|
||||
result = (uint16_t)(I2C_read(1) << 8) | I2C_read(0); // read register content
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
return(result); // return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 write inital configuration and calibration values
|
||||
void INA_init(void) {
|
||||
INA_write(INA_REG_CONFIG, INA_CONFIG); // write INA219 configuration
|
||||
INA_write(INA_REG_CALIB, INA_CALIB); // write INA219 calibration
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 read voltage
|
||||
uint16_t INA_readVoltage(void) {
|
||||
return((INA_read(INA_REG_VOLTAGE) >> 1) & 0xFFFC);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 read sensor values
|
||||
uint16_t INA_readCurrent(void) {
|
||||
uint16_t result = INA_read(INA_REG_CURRENT);
|
||||
if (result > 32767) result = 0;
|
||||
return(result);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
// Millis Counter Implementation for Timer0
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
volatile uint32_t MIL_counter = 0; // millis counter variable
|
||||
|
||||
// Init millis counter
|
||||
void MIL_init(void) {
|
||||
OCR0A = 124; // TOP: 124 = 8000kHz / (64 * 1kHz) - 1
|
||||
TCCR0A = (1<<WGM01); // timer0 CTC mode
|
||||
TCCR0B = (1<<CS01)|(1<<CS00); // start timer0 with prescaler 64
|
||||
TIMSK = (1<<OCIE0A); // enable output compare match interrupt
|
||||
sei(); // enable global interrupts
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read millis counter
|
||||
uint32_t MIL_read(void) {
|
||||
cli(); // disable interrupt for atomic read
|
||||
uint32_t result = MIL_counter; // read millis counter
|
||||
sei(); // enable interrupts
|
||||
return(result); // return millis counter value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Timer0 compare match A interrupt service routine (every millisecond)
|
||||
ISR(TIM0_COMPA_vect) {
|
||||
MIL_counter++; // increase millis counter
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
// Main Function
|
||||
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// Some "strings"
|
||||
const uint8_t mA[] PROGMEM = { 14, 10, 18, 255 }; // "mA "
|
||||
const uint8_t mV[] PROGMEM = { 14, 11, 18, 255 }; // "mV "
|
||||
const uint8_t mW[] PROGMEM = { 14, 12, 18, 255 }; // "mW "
|
||||
const uint8_t mAh[] PROGMEM = { 14, 10, 13, 255 }; // "mAh"
|
||||
const uint8_t mWh[] PROGMEM = { 14, 12, 13, 255 }; // "mWh"
|
||||
const uint8_t SEP[] PROGMEM = { 18, 17, 18, 255 }; // " - "
|
||||
|
||||
int main(void) {
|
||||
// Local variables
|
||||
uint16_t voltage, current, power; // voltage in mV, current in mA, power in mW
|
||||
uint16_t minvoltage = 65535, maxvoltage = 0; // min/max voltages in mV
|
||||
uint16_t mincurrent = 65535, maxcurrent = 0; // min/max current in mA
|
||||
uint16_t minpower = 65535, maxpower = 0; // min/max power in mV
|
||||
uint32_t lastmillis, nowmillis, interval; // for timing calculation in millis
|
||||
uint32_t duration = 0; // total duration in millis
|
||||
uint16_t seconds; // total duration in seconds
|
||||
uint32_t capacity = 0, energy = 0; // counter for capacity in uAh and energy in uWh
|
||||
uint8_t primescreen = 0; // screen selection flag
|
||||
uint8_t lastbutton = 1; // button flag (0: button pressed)
|
||||
|
||||
// Set oscillator calibration value
|
||||
#ifdef OSCCAL_VAL
|
||||
OSCCAL = OSCCAL_VAL; // set the value if defined above
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Setup
|
||||
PORTB = (1<<SETBUTTON); // pullup for set button
|
||||
MIL_init(); // init millis counter
|
||||
I2C_init(); // init I2C
|
||||
INA_init(); // init INA219
|
||||
OLED_init(); // init OLED
|
||||
OLED_clearScreen(); // clear screen
|
||||
lastmillis = MIL_read(); // read millis counter
|
||||
|
||||
// Loop
|
||||
while(1) {
|
||||
// Read sensor values
|
||||
voltage = INA_readVoltage(); // read voltage from INA219
|
||||
current = INA_readCurrent(); // read current from INA219
|
||||
power = (uint32_t)voltage * current / 1000; // calculate power in mW
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate timings
|
||||
nowmillis = MIL_read(); // read millis counter
|
||||
interval = nowmillis - lastmillis; // calculate time interval
|
||||
lastmillis = nowmillis; // reset lastmillis
|
||||
duration += interval; // calculate total duration in millis
|
||||
seconds = duration / 1000; // calculate total duration in seconds
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate capacity in uAh and energy in uWh
|
||||
capacity += interval * current / 3600; // calculate uAh
|
||||
energy += interval * power / 3600; // calculate uWh
|
||||
|
||||
// Update min/max values
|
||||
if (minvoltage > voltage) minvoltage = voltage;
|
||||
if (maxvoltage < voltage) maxvoltage = voltage;
|
||||
if (mincurrent > current) mincurrent = current;
|
||||
if (maxcurrent < current) maxcurrent = current;
|
||||
if (minpower > power ) minpower = power;
|
||||
if (maxpower < power ) maxpower = power;
|
||||
|
||||
// Check SET button and set screen flag accordingly
|
||||
if (PINB & (1<<SETBUTTON)) lastbutton = 0;
|
||||
else if (!lastbutton) {
|
||||
if (++primescreen > 4) primescreen = 0;
|
||||
OLED_clearScreen();
|
||||
lastbutton = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Display values on the OLED
|
||||
switch (primescreen) {
|
||||
case 0: OLED_setCursor(0,0);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(voltage); OLED_printPrg(mV);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(power); OLED_printPrg(mW);
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(0,2);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(current); OLED_printPrg(mA);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(capacity / 1000); OLED_printPrg(mAh);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 1: OLED_setCursor(0,0);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(minvoltage); OLED_printPrg(SEP);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(maxvoltage); OLED_printPrg(mV);
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(0,2);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(mincurrent); OLED_printPrg(SEP);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(maxcurrent); OLED_printPrg(mA);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 2: OLED_setCursor(0,1);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(minpower); OLED_printPrg(SEP);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(maxpower); OLED_printPrg(mW);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 3: // ATtiny25 without decimal places to fit into the flash
|
||||
#if defined(__AVR_ATtiny25__)
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(32,0);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(capacity / 1000); OLED_printPrg(mAh);
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(32,2);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(energy / 1000); OLED_printPrg(mWh);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(16,0);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(capacity / 1000); OLED_printChar(DECIMAL);
|
||||
OLED_printDec12(capacity % 1000); OLED_printPrg(mAh);
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(16,2);
|
||||
OLED_printDec16(energy / 1000); OLED_printChar(DECIMAL);
|
||||
OLED_printDec12(energy % 1000); OLED_printPrg(mWh);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 4: OLED_setCursor(32,1);
|
||||
OLED_printDec8(seconds / 3600); OLED_printChar(COLON);
|
||||
seconds %= 3600;
|
||||
OLED_printDec8(seconds / 60 ); OLED_printChar(COLON);
|
||||
OLED_printDec8(seconds % 60 );
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default: break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
_delay_ms(100);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
|||
# Type "make help" in the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
# Input and Output File Names
|
||||
SKETCH = USB_Tester_v1.2.ino
|
||||
SKETCH = USB_Tester_v1.3.ino
|
||||
TARGET = usb_tester
|
||||
|
||||
# Microcontroller Options
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue